World news
AFD, AFRICA, AFRICAN NATIONAL CONGRESS, AP, ASIA, BOTSWANA, BRITAIN, CAS MUDDE, DEMOCRACY, ELECTION, EUROPE, EUROPE/ASIA, FRANCE, GEORGIA, GERMANY, GHANA, GOVERNMENT, INDIA, JAPAN, LONDON, MIDDLE EAST, MOZAMBIQUE, NA, NAMIBIA, NORTH AMERICA, OPPOSITION, POLITICS, POPULISM, ROB FORD, ROMANIA, RUSSIA, SENEGAL, SOUTH AFRICA, SOUTH AMERICA, SOUTH KOREA, SWAPO, UKRAINE, UNITED KINGDOM, UNITED STATES, UNIVERSITY OF, URUGUAY, YAMANDÚ ORSI
Oliver Grayson
0 Comments
2024 Elections: A Global Rejection of Incumbent Leadership
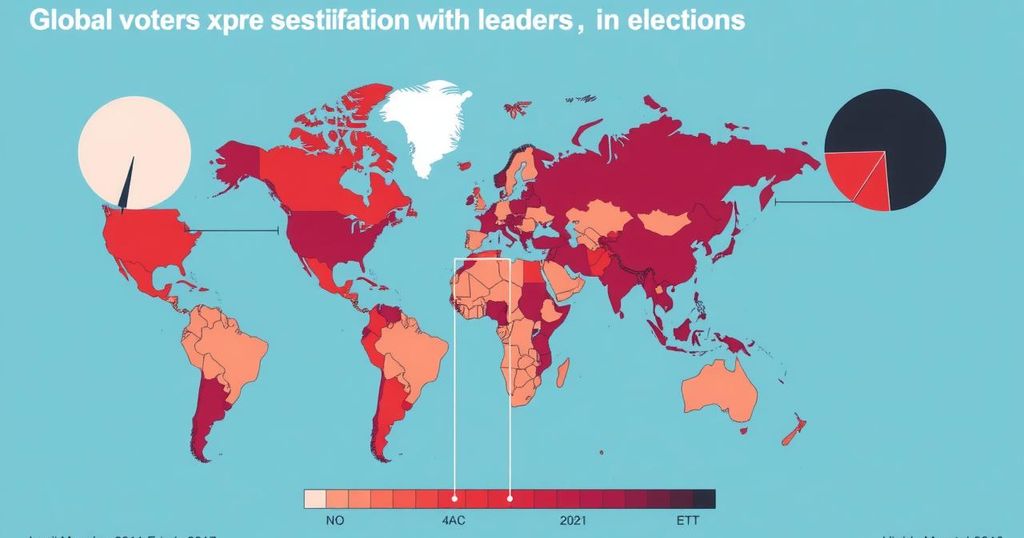
In 2024, voters worldwide expressed their discontent by ousting numerous incumbents across over 70 countries, driven by economic frustration and political instability. Significant electoral shifts occurred in nations such as India, the United States, and South Africa, reflecting a pronounced desire for change. The year was characterized by the rise of populist and far-right movements, indicating a growing trend towards challenging established political norms amidst widespread dissatisfaction.
The global electoral landscape in 2024 witnessed significant political upheaval, with a palpable rejection of incumbent governments across numerous nations. Voter sentiments indicated a decisive call for change, responding to widespread dissatisfaction fueled by economic instability, high inflation, and the lingering impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. Notable examples include dramatic electoral outcomes in countries such as India, the United States, and South Africa, where traditional power dynamics shifted under the weight of public discontent. As leaders were ousted or faced unexpected defeats, including Prime Minister Narendra Modi in India and long-standing parties in various African nations, the results illustrated a desire for new governance amid growing frustration with existing political structures.
Throughout the year, dissatisfaction with incumbents culminated in significant electoral results across over 70 nations, home to half of the global population. Established political parties, from Britain’s Conservatives to Japan’s Liberal Democratic Party, faced electoral defeats, often leading to unprecedented shifts in power dynamics. Concurrently, the emergence of populist and far-right parties reflected an ongoing trend, with proposals reminiscent of nationalistic resistance to current challenges amplified by economic hardships and displacement resulting from international conflicts.
In 2024, global elections were marked by heightened voter dissatisfaction towards existing governments, a sentiment intensified by economic strife, inflation, and the repercussions of the pandemic. The rise of anti-incumbent sentiments can be viewed as a response to perceived governmental failures in addressing pressing social, economic, and political issues. Political analysts suggest that this electoral climate was characterized by an increasing allure of outsider candidates and populist movements, as voters sought alternatives to traditional governance that appeared ineffective in mitigating their grievances. This backdrop shaped major political developments worldwide, revealing fractures within democratic systems and raising concerns regarding future governance.
The electoral events of 2024 underscored a significant shift in the political landscape across numerous nations, indicating a global populace weary of traditional political leadership. As incumbents were ousted and new, often populist candidates emerged, the findings reflect a yearning for change amidst ongoing economic challenges. This wave of anti-establishment sentiments suggests an evolving dialogue surrounding democracy, where citizens express their desire for effective governance but often find themselves disillusioned by the realities of political practice. Insights gained from these elections will be pivotal for understanding ongoing trends in global political behavior.
Original Source: www.pbs.org



Post Comment